Key Takeaways: Generative AI
- Creative Core: Unlike conventional AI, Generative AI creates completely new and original pieces of work such as text, pictures, computer programs, or sound.
- Neural Architecture: These systems are based on sophisticated methods of deep learning (e.g., Transformers and Diffusion architectures) that predict likely next elements in a sequence.
- Increased Productivity: By 2026, Generative AI will be commonly used by both developers and businesses for tasks such as automating repetitive code, creating content, etc..
- Human-Like Output: These systems produce results that resemble human thought processes and/or human creativity by learning relationships between items in large datasets.
- Competitive Edge: Early adoption allows organizations to reduce time-to-market, scale creativity without increasing headcount, and provide 24/7 automated customer support.
- Potential Risk: Implementation requires monitoring for AI “hallucinations,” complying with data privacy laws, addressing ethical biases, and ensuring human oversight.
- Key to Realizing Value: Maximum value is achieved when using high-quality and domain-specific data to use and integrate generative AI within an organisation as an assistant.
Generative AI has quickly progressed from being a research-oriented idea to now what can be considered as a practical source of technology. It is changing the way people interact with and utilize their capabilities, through transforming processes that have traditionally been human. This includes generating human-like text and images (in addition to assisting software developers) as well as creating new types of output such as music by automating the content creation process. Generative AI is helping to shape how society will innovatively influence the future through technology-driven solutions.
In this complete guide, we’ll explain what is generative AI, how it works, how it differs from traditional AI, real-world generative AI examples, and its most impactful business and software development use cases in 2026.
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to a category of artificial intelligence wherein systems create new types of content (for example – text, images and audio) by using large-scale datasets to derive pattern recognition.
Unlike rule-based systems, generative AI does not simply follow predefined instructions. Instead, it learns from examples and produces original outputs that closely resemble human-created content.
When people ask “what is generative AI”, the simplest answer is:
Generative AI is AI that creates, not just analyzes.
How Generative AI Works
It’s critical to comprehend how Generative AI works in order to fully appreciate its benefits. Fundamentally, generative AI uses sophisticated machine learning solutions that have been trained on enormous datasets to find relationships, context, and patterns. AI responses feel organic, relevant, and imaginative thanks to these models’ use of probability and prediction to produce new outputs that closely resemble content produced by humans. The power of generative AI can be better understood by comprehending how it operates.
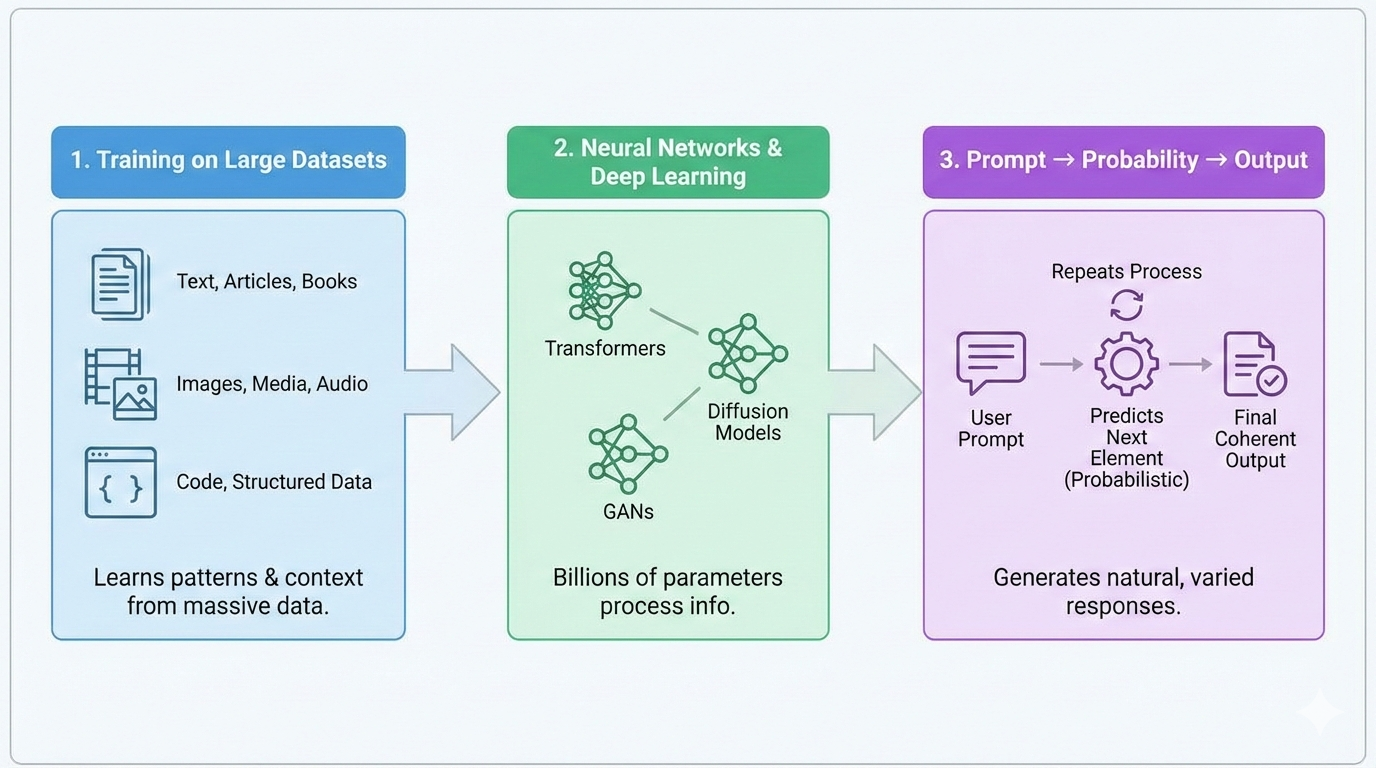
Fundamentally, generative AI uses sophisticated machine learning solutions trained on enormous datasets to understand relationships, context, and patterns, building on advances in modern generative models that generate new outputs using probability and prediction.
1. Training on Large Datasets
Most generative AI systems rely on advanced deep learning architectures such as Transformers, Diffusion models, and GANs, which are actively evolving through ongoing generative AI research
across the AI community.
Generative AI models are trained on massive datasets such as:
- Text from articles, books, and websites
- Images, videos, and audio samples
- Code repositories and structured data
The model learns relationships, context, and patterns within the data.
2. Neural Networks & Deep Learning
Most generative AI systems rely on deep learning architectures such as:
- Transformers
- Diffusion models
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
These models use billions of parameters to understand context and generate realistic outputs.
3. Prompt → Probability → Output
When a user gives a prompt:
- The model predicts the most likely next element (word, pixel, sound, or code)
- It repeats this process thousands of times
- A complete, coherent output is generated
This probabilistic approach is why outputs feel natural but may vary each time.
Generative AI vs Traditional AI
The comparison between generative AI vs traditional AI helps clarify why generative systems are gaining rapid adoption across industries. Generative AI goes one step further by creating completely original content, whereas traditional AI concentrates on classification, prediction, and rule-based automation. Businesses can now automate complex tasks that previously required human creativity and reasoning thanks to the transition from “decision-making AI” to “creative AI.” One of the most common comparisons is generative AI vs traditional AI.
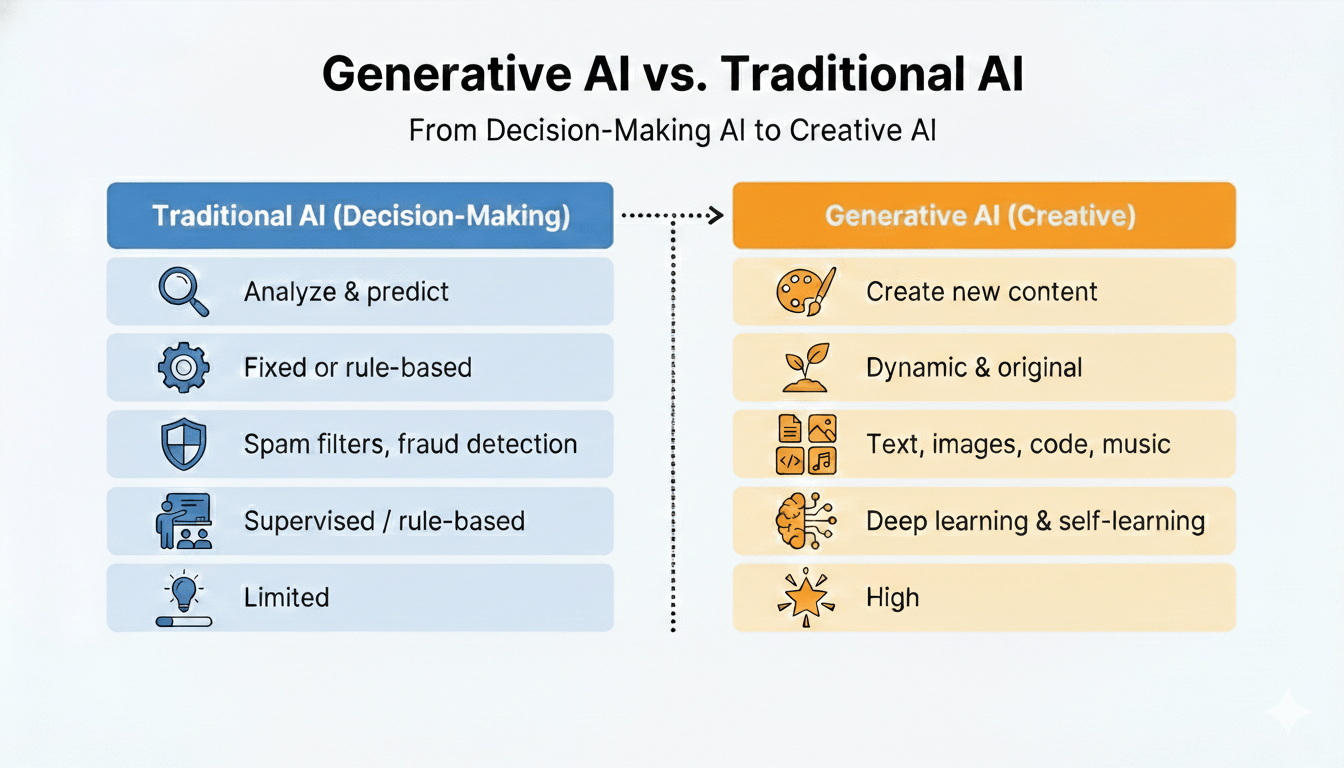
Traditional AI answers questions like “Is this spam?”
Generative AI answers questions like “Write an email, design an image, or generate code.”
To deeply understand how generative AI fits into the broader artificial intelligence landscape and why it differs fundamentally from traditional approaches, check McKinsey’s explainer on generative AI.
Generative AI Examples (Real-World)
Real-world generative AI examples show how this technology is already incorporated into commonplace applications. Generative AI is now operational rather than experimental, from AI chatbots and content creation tools to image creation and software development assistants. These illustrations show how companies and artists are utilizing generative AI to boost output, cut expenses, and spur creativity:
Text Generation
- Blog writing and SEO content
- Chatbots and AI voice agents
- Email drafting and summarization
Image & Design Generation
- Marketing creatives
- UI/UX design concepts
- Game assets and illustrations
Code Generation
- Frontend and backend code snippets
- Bug fixing and optimization
- API documentation
Audio & Video Generation
- AI voiceovers
- Virtual assistants
- Synthetic training videos
Generative AI Use Cases in Business
The growing adoption of generative AI use cases in business shows how organizations are moving beyond experimentation to full-scale implementation. Businesses are using generative AI to improve customer service, automate marketing, expedite sales, and produce business insights. Business operations are changing as generative AI use cases become more prevalent.
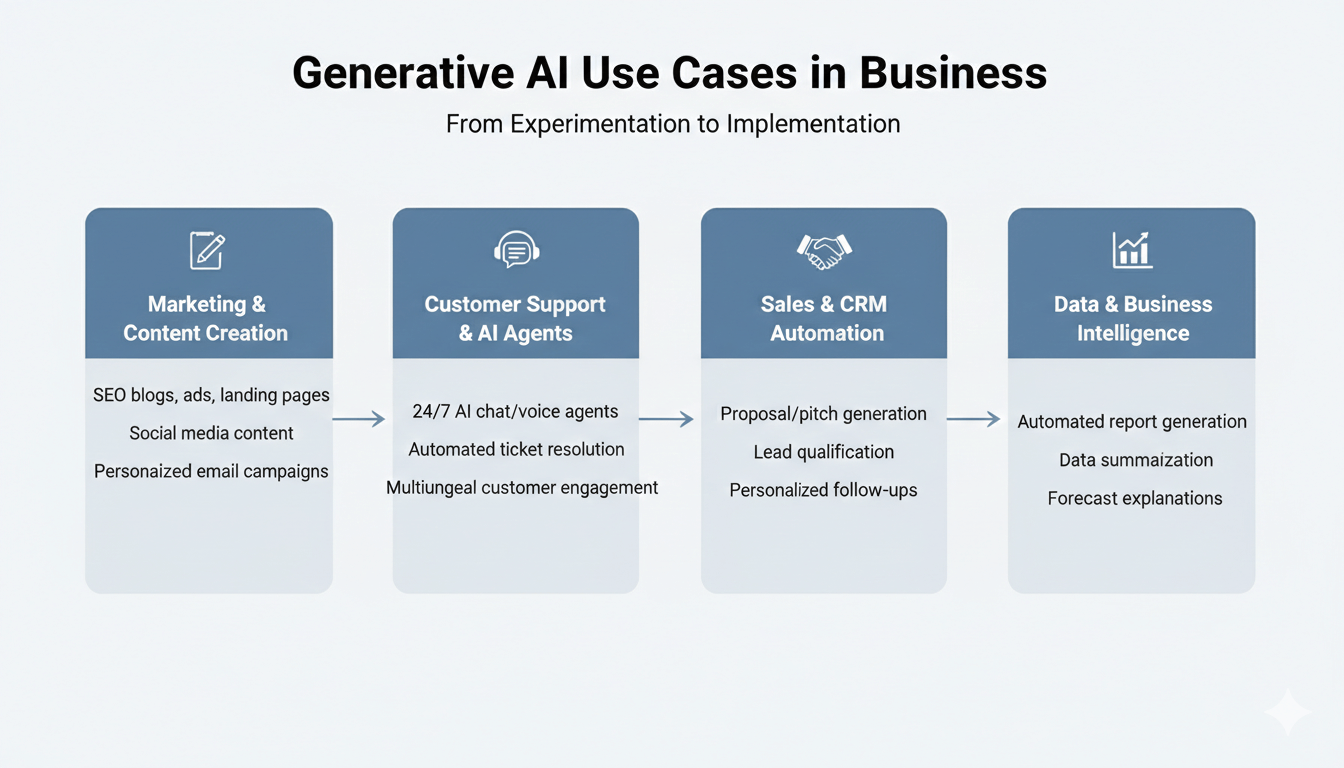
1. Marketing & Content Creation
- SEO blogs, ads, and landing pages
- Social media content at scale
- Personalized email campaigns
2. Customer Support & AI Agents
3. Sales & CRM Automation
- Proposal and pitch generation
- Lead qualification using AI conversations
- Personalized follow-ups
4. Data & Business Intelligence
- Automated report generation
- Data summarization for decision-makers
- Forecast explanations in natural language
Generative AI Applications in Software Development
Generative AI applications in software development, where AI development services boost developers’ productivity, are among the most revolutionary fields. Writing code, debugging, performance optimization, and even converting designs into usable interfaces are all made easier by generative AI. In 2026, development teams increasingly rely on generative AI to reduce development time, improve code quality, and accelerate product delivery.
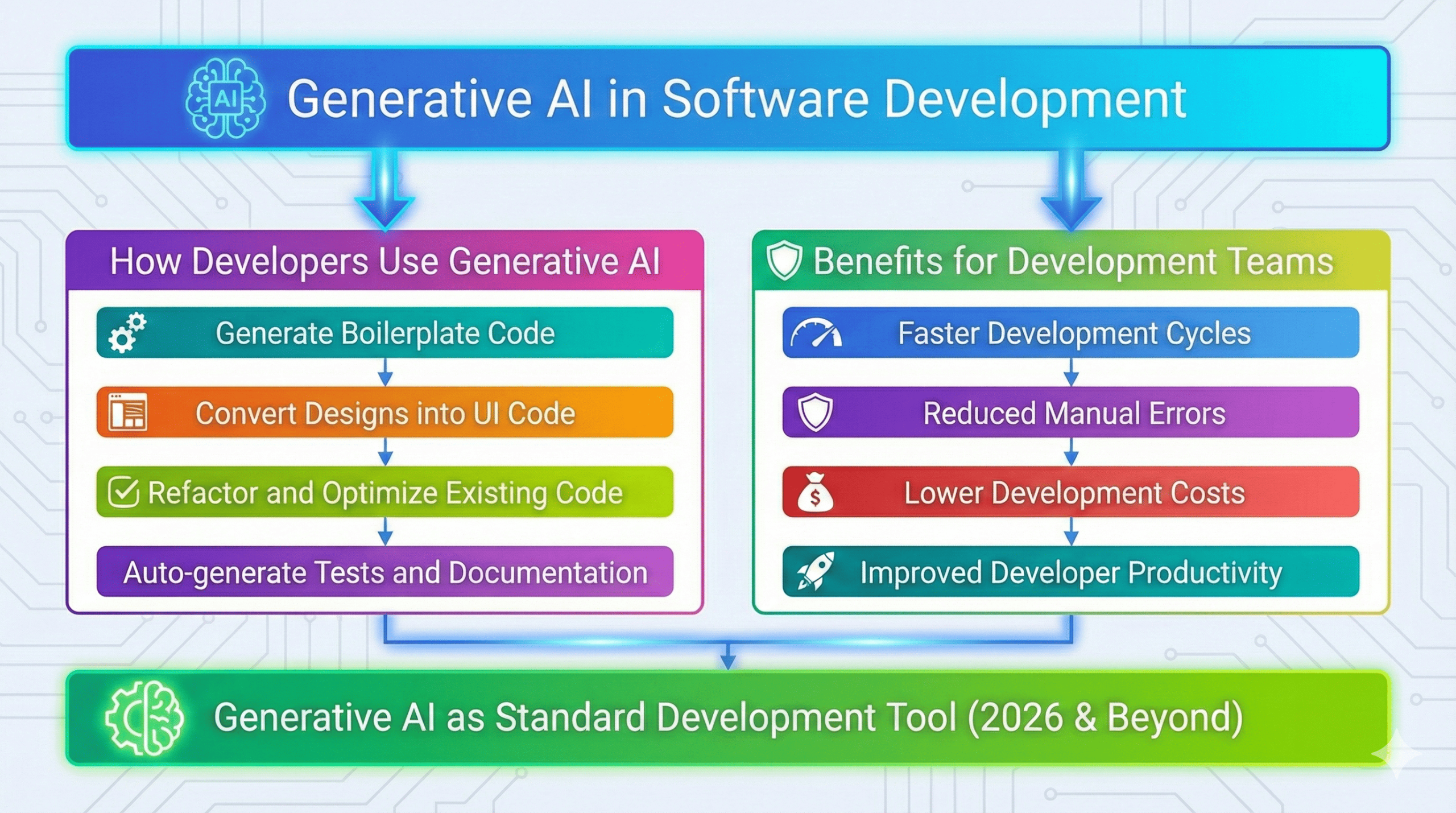
How Developers Use Generative AI
- Generate boilerplate code
- Convert designs into UI code
- Refactor and optimize existing code
- Auto-generate tests and documentation
Benefits for Development Teams
- Faster development cycles
- Reduced manual errors
- Lower development costs
- Improved developer productivity
In 2026, generative AI is no longer optional—it’s becoming a standard development tool.
Why Generative AI Matters in 2026
The potential of generative AI to close the gap between human creativity and machine efficiency is what will make it significant in 2026. Businesses require quicker innovation cycles, customized user experiences, and economical scaling as the competition in the digital space heats up. These needs are satisfied by generative AI, which makes it possible for intelligent automation, quick content production, and AI-powered decision support in a variety of sectors.
According to Gartner, more than 80% of enterprises are expected to use generative AI APIs in production applications by 2026, highlighting how rapidly generative AI is becoming a core business technology.
Source: Gartner generative AI forecast
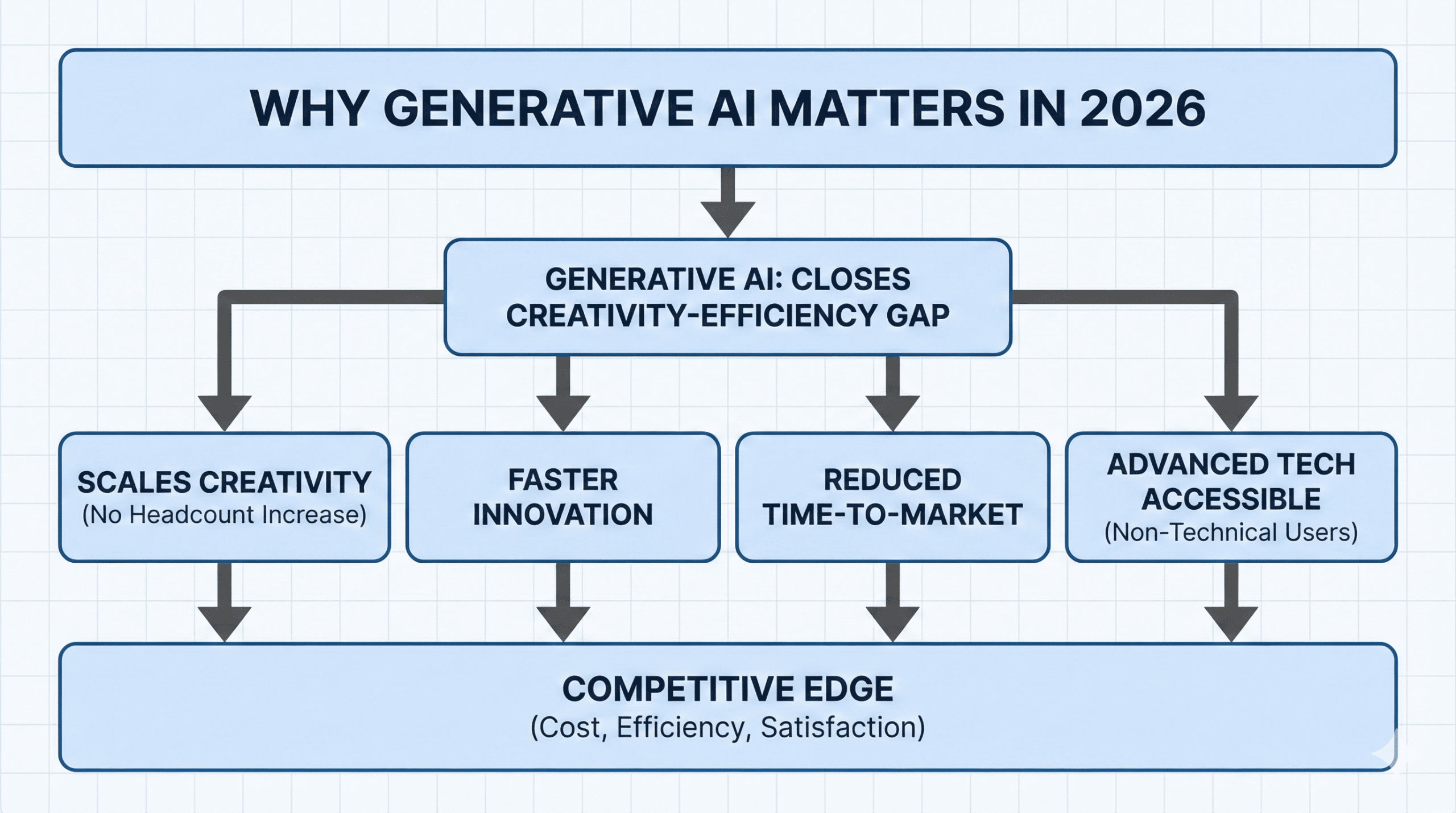
Today, generative AI is essential because it
- Scales creativity without increasing headcount
- Enables faster innovation
- Reduces time-to-market
- Makes advanced technology accessible to non-technical users
Early generative AI adoption gives businesses a competitive edge in terms of cost, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Limitations of Generative AI
Despite its advantages, responsible adoption of generative AI requires an awareness of its drawbacks. Issues such as hallucinated outputs, data privacy risks, ethical concerns, and dependence on training data highlight the limitations of generative AI and the need for careful management. To ensure reliability and compliance, businesses implementing generative AI must establish safeguards, validation workflows, and human oversight rather than relying solely on automated systems.
.
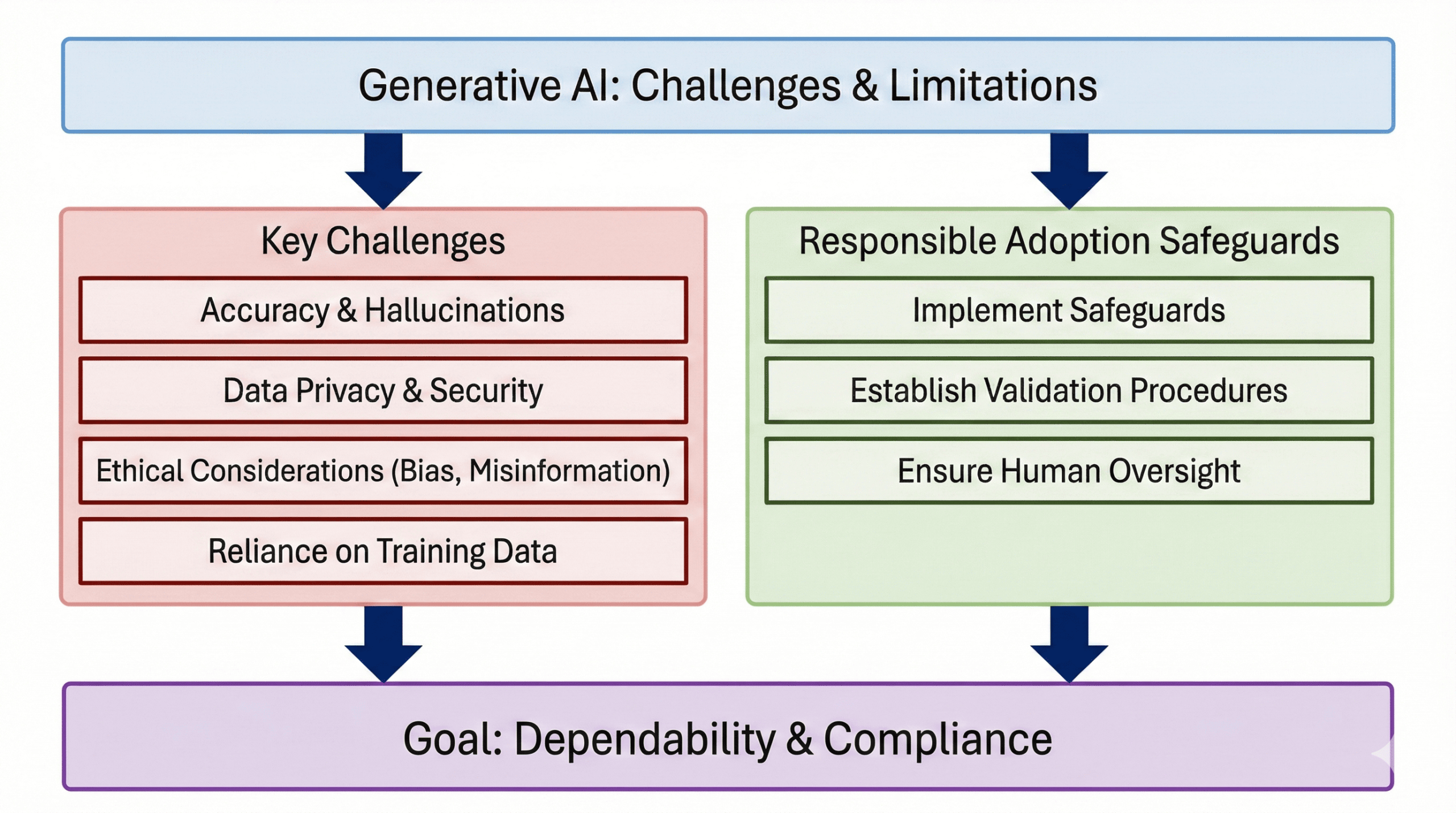
Generative AI has limitations despite its strength:
1. Accuracy & Hallucinations
A common limitation of generative AI systems is AI hallucinations – where the model generates outputs that appear plausible but are factually incorrect or misleading.
2. Data Privacy & Security
Sensitive data must be handled carefully to comply with regulations.
3. Ethical Considerations
Bias, misinformation, and misuse require responsible AI practices. UNESCO Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence
4. Human Oversight Is Essential
Generative AI should assist humans, not fully replace critical decision-making.
Best Practices for Using Generative AI
To help organizations realize the greatest possible returns on its investment in Generative AI, best practice processes must be employed. Organisations must employ best practices to ensure high-quality training related to the right models used, continual monitoring of outputs from developed models, and the appropriate combination of AI automation along with human judgement. This can provide an opportunity within an organisation to deploy Generative AI systems that provide accuracy, scalability, and alignment to the organisation’s goals and objectives in the real world. To get maximum value from generative AI:
- Use high-quality, domain-specific data
- Combine AI outputs with human review
- Monitor performance continuously
- Apply clear governance and compliance rules
Concluding Note
The development of software, content, and digital experiences has fundamentally changed as a result of generative AI, which is no longer merely a fad. Businesses can achieve new heights of productivity and creativity by comprehending what generative AI is, how it operates, and how it varies from traditional AI. Its influence is evident in a variety of industries, from powerful generative AI use cases in software development and business to real-world examples. Organizations that strategically implement generative AI will have a major competitive advantage as 2026 progresses. Generative AI can turn concepts into scalable solutions and promote long-term company growth with the correct strategy, oversight, and knowledge.
Ready to leverage generative AI for your business?