Over the last few years, Artificial Intelligence has transformed from being simple to implement wherein users had only to provide basic prompts like “Write me a blog about XYZ’ to having AI act autonomously by being able to think, reason, plan, create and execute complex tasks on its own. This has led to a divided opinion regarding which is best suited for contributing value to today’s businesses; generative AI or agentic AI.
The two types of AI are very similar but operate differently. Generative AI generally is focused on creating “stuff (content)” whereas agentic AI is purpose-driven to accomplish a goal through structured processes. Businesses looking to implement some form of automation will do well to familiarize themselves with the distinctions between agentic AI vs generative AI since they represent fundamentally different tools for automation purposes.
We will take an in-depth look into the various kinds of AI and how they differ from each other as well as share real examples of the various AI technologies that are applicable across the spectrum of business today, tomorrow (2026), and what to expect in the future.
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a member of the class of AI software that was designed to produce new content by analyzing a set of existing patterns. Everything from text documents (articles, reports, etc.), images (photos, artwork), computer programming code, audio (music, podcast), etc, may be generated using generative AI.
Most forms of generative AI rely on a set of data, known as large language models (LLMs), to generate realistic text output from existing LLM databases that contain millions of records of text. The unique ability of LLMs to analyze this volume of text and learn how to determine the appropriate next word or token based on mathematical probability allows them to create outputs that are human-like and sound natural.
Most currently available generative AI programs operate based on the prompt-driven model; this means that the user provides the program with instructions, to which the program then generates corresponding outputs. The interaction with generative AI tends to be simple (input/output).
For companies looking into the applications of AI, Gartner offers information on the role of generative AI in transforming content generation, research, and productivity applications.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is an advanced level of AI development. Whereas, prior systems would react to requests for assistance. Agents can both make and follow through on decisions they make (based on a defined goal and a previously defined end state).
Autonomous Agents (agentic AI) interpret the goals defined for them by their human operators (or through another agent’s actions) into multiple executable tasks and perform these tasks using a determined process. They control multi-step AI workflows, and can determine the success of the current task by comparing past results with the current results and use that information to alter their next step or goal.
Agentic AI continues to build upon the generative foundation of previous systems to help build the reasoning engine for agentic systems from large language models (LLMs). Generative AI can be an important part of the agentic AI system’s reasoning process. However, to enable agents to successfully complete their defined goals, agents are also built with planners, memory modules and other tools that interface with cloud/software systems (e.g., APIs) and databases.
Because of the manner in which agentic systems are architected to include numerous systems, agentic AI have many similarities. However, they are also fundamentally different as agentic AI systems are “Intelligent AI Decision Making Systems” that continue to pursue an objective until it is achieved.
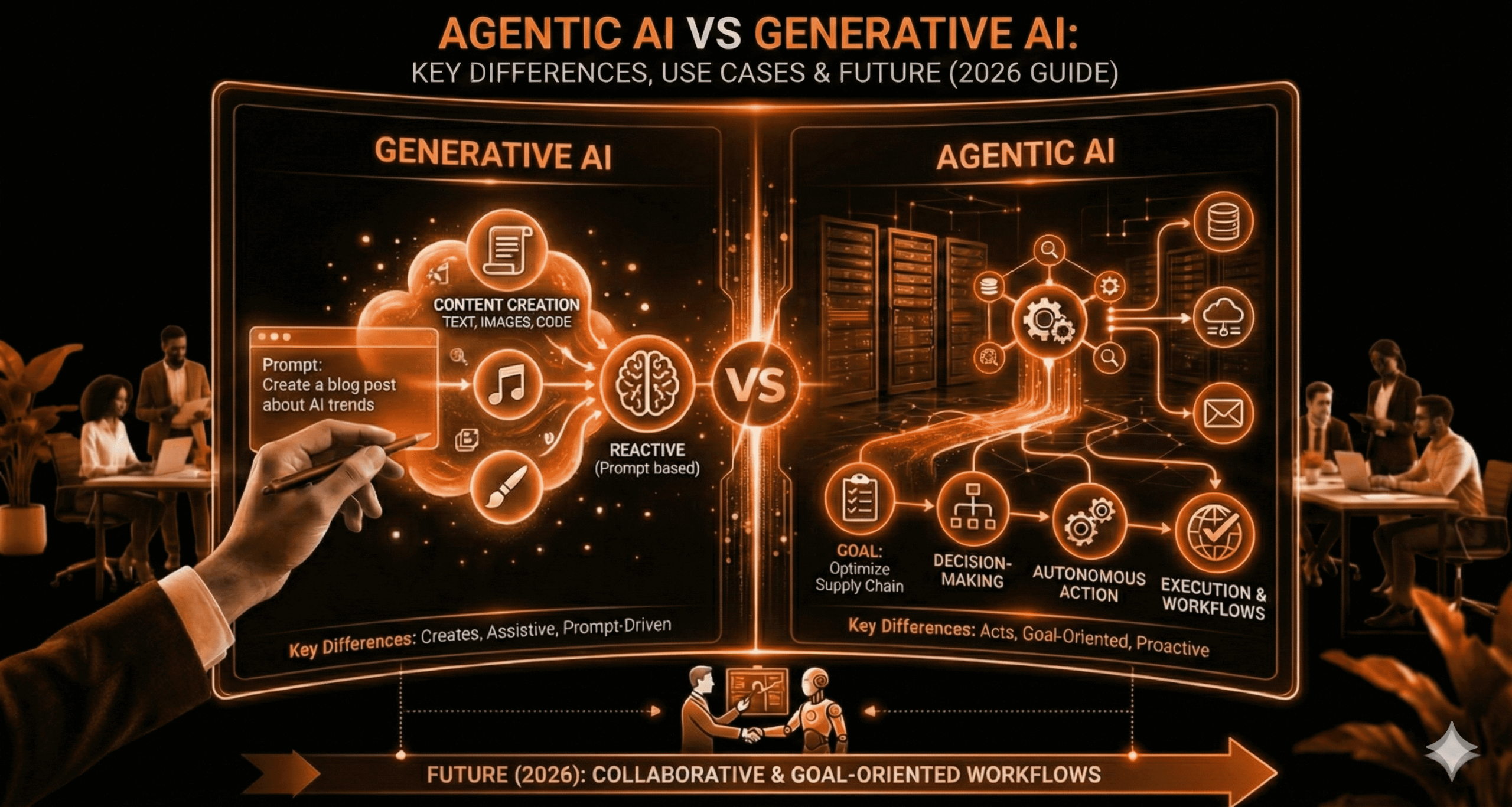
Core Differences Between Agentic AI and Generative AI
Most of the discussion surrounding agentic AI vs generative AI has to do with autonomy.
Generative AI is typically focused on generating content (i.e., producing an output from an input request). Generative AI generates an output and does not track the success of previous tasks nor create plans or manage long-lived tasks.
Agentic AI is focused on goal achievement. Agentic AI will plan and execute, assess, and adapt to what they are attempting to achieve based upon the output generated by previous actions. For instance responding to other agent actions, assessing if the agent was able to fulfill its task.
As a notable example of the difference between generative AI and agentic AI, generative AI will assist in generating new content/elements (in many forms) while agentic AI will provide assistance in completing tasks.
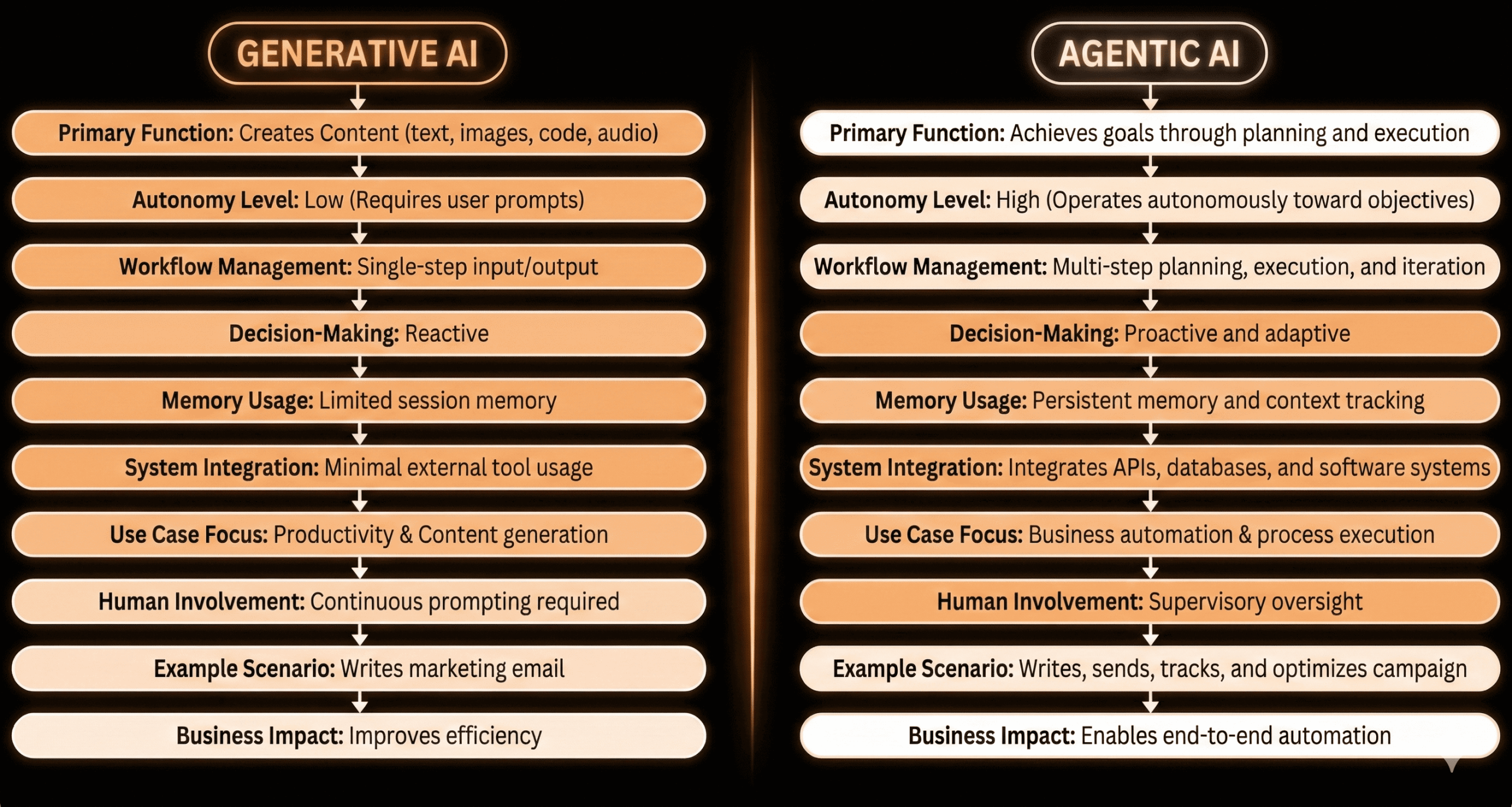
| Feature |
Generative AI |
Agentic AI |
| Primary Function |
Creates content (text, images, code, audio) |
Achieves goals through planning and execution |
| Autonomy Level |
Low – Requires user prompts |
High – Operates autonomously toward objectives |
| Workflow Management |
Single-step input/output |
Multi-step planning, execution, and iteration |
| Decision-Making |
Reactive |
Proactive and adaptive |
| Memory Usage |
Limited session memory |
Persistent memory and context tracking |
| System Integration |
Minimal external tool usage |
Integrates APIs, databases, and software systems |
| Use Case Focus |
Productivity & content generation |
Business automation & process execution |
| Human Involvement |
Continuous prompting required |
Supervisory oversight |
| Example Scenario |
Writes marketing email |
Writes, sends, tracks, and optimizes campaign |
| Business Impact |
Improves efficiency |
Enables end-to-end automation |
Architectural Differences
In structural terms, generative AI systems are built on large language model (LLM) architecture. A trained model receives input, generates output, but ultimately has no formal persistent workflow management or an inherent means of executing that workflow.
On the other hand, agentic AI systems consist of various layers. In addition to their reasoning engines, agentic AIs have additional components to support planning, memory storage, integration of tools, and other functions. Hence, the architecture of agentic AIs allows them to function as full, end-to-end AI planning and executing systems for all types of activities.
Where generative AIs output a single result for each task, agentic AIs operate constantly. Agentic AIs will assess a given situation, determine an action to take, execute that action, assess the outcome of that action and repeat this process until the desired result is achieved.
This architectural shift is a key enabler of the evolution of agentic AIs from being assistive technologies, into being automating technologies.
Decision-Making and Autonomy
Another major point of differentiation is the way in which decision making occurs.
Generative AIs generate an output based on inputs from training data; they will not assess whether the generated output was able to accomplish any type of larger objective unless specifically instructed to do so.Agentic AIs are designed to continuously monitor their performance and the outcomes of their previous decisions in real-time through machine learning-driven automation. Agentic AIs will assess both their individual performance and that of their entire system or process, compare their current outcomes to previously established goals or objectives, and modify their behavior or execution strategy based on that assessment, often without explicit instruction from a human.
As a result of these capabilities, agentic AIs provide significant advantages to organizations operating in environments that require continuous adaptability, efficiency and effectiveness.
Business Applications
Generative AI has already created measurable effects in business environments. Marketing departments utilize generative AI to produce blog posts, advertisements, and email campaigns. Customer service departments hire AI chatbots to answer common questions. Internal teams apply it to assist with documentation and research.
Many businesses looking to transform deeper are now utilizing agentic AI for enterprise AI automation.
Instead of assisting with creating content, agentic AI systems automate entire workflows. For example, they automate activities such as qualifying leads by updating CRM systems. They create and deliver personalized outreach messages, and track performance metrics automatically. For instance, finance departments settle transaction discrepancies and highlight anomalies with agentic AI. Similarly, HR departments are able to manage the onboarding process across multiple systems through the use of agentic AI.
This instance clearly shows how AI has evolved from supporting content creation to taking action to automate processes.
Software Development and Technical Workflows
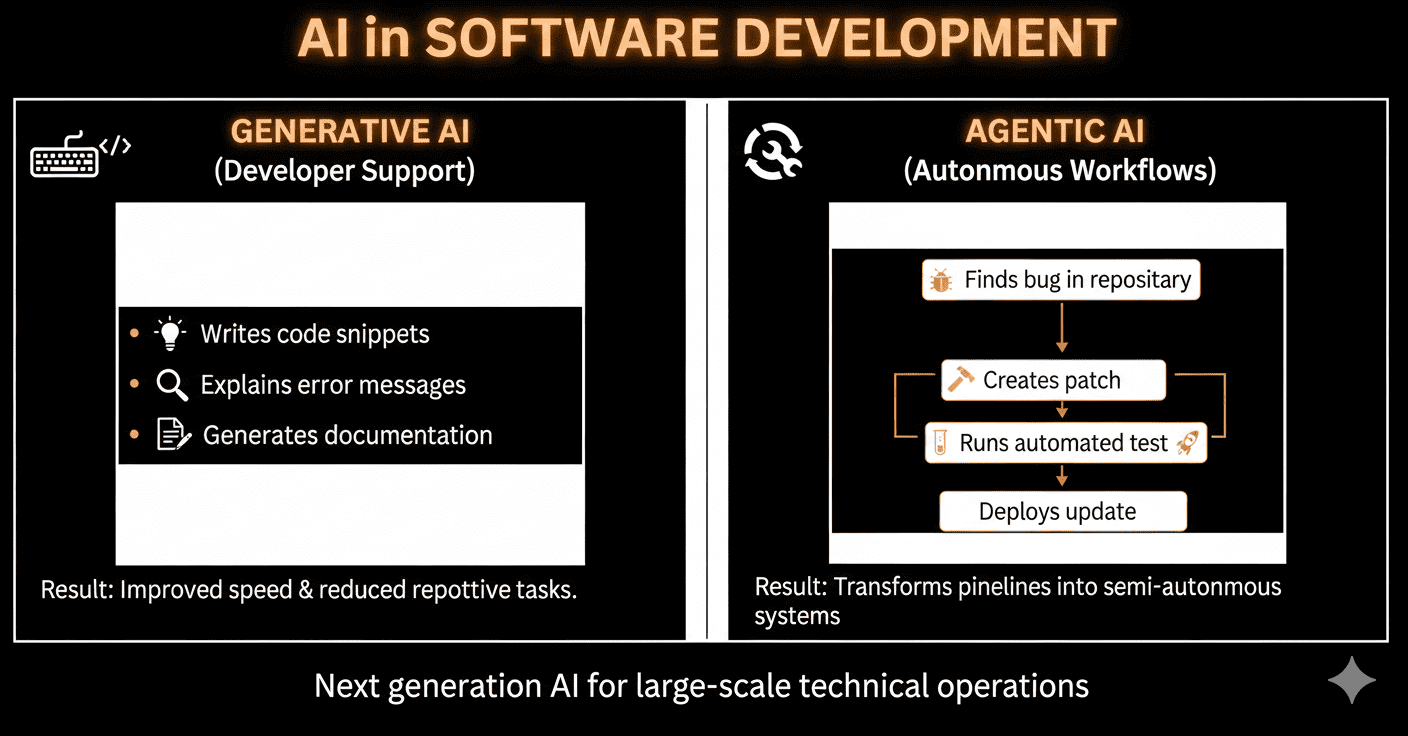
The difference between agentic vs generative AI is very distinguishable with regard to software development.
For software developers, generative AI has many functions. These include writing code snippets, providing explanations for error messages, and generating documentation. The result is improved speed and reduced repetitive tasks.
However, agentically managed technical workflows are what distinguish agentically managed workflows from generatively managed workflows. For example, while generative AI would help find a bug in a repository, agentic AI would automatically create a patch. It would run an automated test to validate the output, and deploy the update. Agentic AI transforms technical development pipelines into semi-autonomous systems by arranging structured multi-step AI workflows.
These developments represent the next generation of AI systems that will provide strong support for large-scale technical operations.
Enterprise AI Automation Trends in 2026
As we look toward 2026, the time for experimentation is over. The organizations are now implementing automated AI into their enterprise operations at scale. Enterprise AI will be treated as a strategic priority instead of simply a pilot program.
Companies are using agent-based frameworks to combine generative AI with execution and memory layers to enhance their use for LLMs instead of replacing them. This creates greater opportunities for cross-system integration of AI-enabled automation tools to connect to various business applications in a seamless manner.
At the same time that companies are expanding their use of autonomous AI agents with increased access to operational systems. They are establishing governance and monitoring systems. Along with compliance measures, to ensure that their use of AI is done in an ethical and responsible manner.
Challenges and Risks
Challenges exist for generative AI and for agentic AI.
Some of the descriptions of the “hallucinations” produced by generative AI create inaccuracies or misleading outputs. a risk category also outlined in the NIST AI Risk Management Framework. This means a human must always be involved in reliable and valid decisions at critical stages. There are also data and intellectual property considerations with generative AI that must be handled with care.
With agentic AI, a new layer of complexity has introduced both benefits and challenges. Specific to the enterprise environment, agentic AI systems can perform actions. Hence processes to maintain durability and to deliver accurate results for the enterprise through agentic AI are needed.
One of the key challenges in adopting advanced AI will be balancing autonomy and accountability.
The Future of Agentic and Generative AI
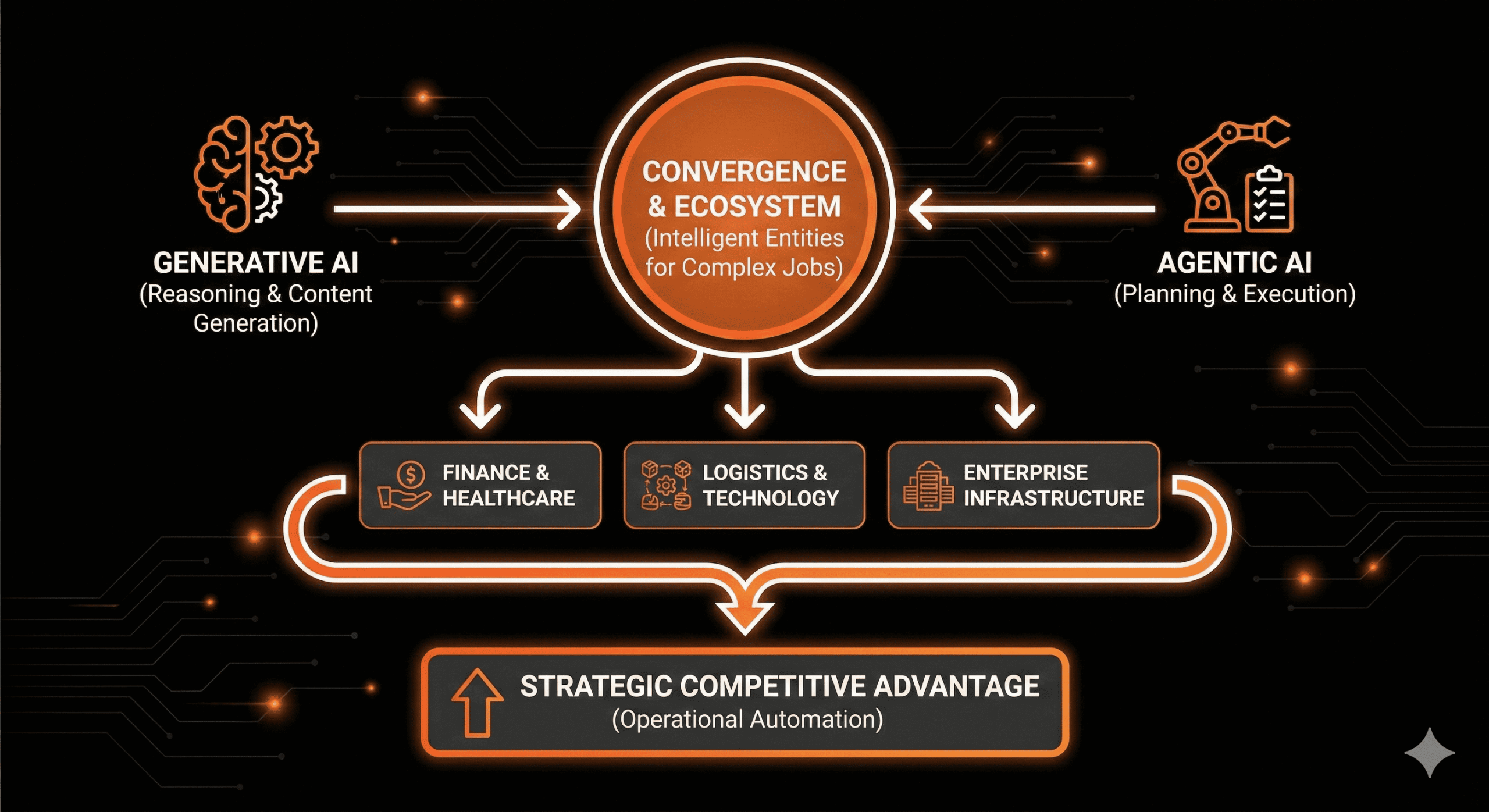
There is no longer a choice to make between agentic AI and generative AI. The future will involve a convergence of both types of systems.
Generative AI will assist with reasoning and content generation. With an agentic framework for planning, persistence, and execution; ultimately building an ecosystem of intelligent entities able to handle increasingly complex job functions.
We can expect the widespread implementation of autonomous agents across multiple industries over the next few years. These include finance, healthcare, logistics, and technology. Planning and executing systems for AI will become more industry-focused, reliable, and integrated into enterprise infrastructures.
As these emerging technologies continue to mature, organizations that leverage generative AI with operational automation strategically will have a competitive advantage.
Wrapping Up
When we think about agent AI vs generative AI as revolutionary ways of doing something. We see that generative AI is focused on generating something. While agent AI is primarily focused on performing/executing whatever’s generated.
Whether an organization is looking to implement generative AI or agent AI, both technologies have the ability to substantially change the way organizations operate.
The most critical factor in each of these two ways of approaching AI is determining which one is a good fit for their specific organization.
If an organization can determine when to use generative content-producing AI versus when to use agent AI. And the way to implement accordingly will continue to be leaders in the next generation of digital transformation.
Ready to Start Developing Advanced AI Solutions?
If your organization is interested in building generative AI solutions or developing intelligent agent AI systems, consider our AI Development Services.
Looking to implement AI in your business? ChicMic helps companies build both generative and agent-based AI systems.